算法课的第一次实验。
实验内容:渗透问题
关于环境
由于需要用到课程给的库里面的函数,所以需要先把课程给的包 algs4.jar 导入。
对于 IDE,我并没有使用课程推荐的 Drjava 和 IntelliJ,而是用了大一下学 Java 时所用的 Eclipse。
问题分析
发现问题是让我们在一个初始所有格点都为 block 状态的 $N \times N$ 的网格上随机地选一个点使其变为 open 状态,如此重复操作直至第一行存在 open 格点 $x$ 和 $y$ ,分别位于第一行和最后一行,它们位于同一个连通块中。
连通块,自然想到用并查集来维护,每次把一个点变成 open 状态时,把其上下左右的 open 格点与其 Union 。
为了方便编写,考虑把 $N\times N$ 的网格映射到一个一维数组上,可以这样映射:第 $i$ 行第 $j$ 列 $\to$ 第 $(i-1)\times N+j$ 个值。这样,就映射到了 $1\sim N^2$ 上。
类似于最短路问题的“超级源点”,考虑把 $0$ 和 $N^2+1$ 设为超级源点,第一行所有格点变为 open 状态时,除了与上下左右的 open 格点 Union ,还与 $0$ 号 Union;最后一行同理,与 $N^2+1$ 格点 Union。
实验要求比较朴素并查集与按秩合并并查集的效率。于是考虑写一个朴素并查集类 QuickFind 和按秩合并并查集类 WeightedQuickUnion 。
于是便可以按照文件中所写的那样,建立一个 Percolation 类,利用两个并查集类。
蒙特卡洛模拟部分,直接按照文件中给的函数实现对应的功能就行了。计算均值、标准差、置信区间需要调用 algs4.jar 库里面的函数,直接 import 即可。
代码
没怎么写过 Java ,写的很丑(
QuickFind 类
package percolation;
public class QuickFind {
private int n;
private int[] id;
public QuickFind(int n) {
this.n = n;
id = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) id[i] = i;
}
public int Find(int p) {
return p == id[p] ? p : Find(id[p]);
}
// public boolean Connected(int u,int v) {
// return Find(u) == Find(v);
// }
// public void Union(int u, int v) {
// int fu = Find(u), fv = Find(v);
// id[fv] = fu;
// }
public boolean Connected(int u,int v) {
return id[u] == id[v];
}
public void Union(int u, int v) {
int fu = id[u], fv = id[v];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(id[i] == fv) id[i] = fu;
}
}
}
注释部分为路径压缩的写法。
WeightedQuickUnion 类
package percolation;
public class WeightedQuickUnion {
private int n;
private int[] id, sz;
public WeightedQuickUnion(int n) {
this.n = n;
id = new int[n];
sz = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
id[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
}
public int GetN() {
return n;
}
public int Find(int p) {
while(p != id[p]) p = id[p];
return p;
}
public boolean Connected(int u, int v) {
return Find(u) == Find(v);
}
public void Union(int u, int v) {
int fu = Find(u), fv = Find(v);
if(fu == fv) return ;
if(sz[fu] < sz[fv]) {
id[fu] = fv;
sz[fv] += sz[fu];
}
else {
id[fv] = fu;
sz[fu] += sz[fv];
}
n--;
}
}
Percolation 类
package percolation;
public class Percolation {
private int n, opt;
private int[][] a;
private final int[] dx = {0, 0, 1, -1};
private final int[] dy = {1, -1, 0, 0};
private QuickFind qf;
private WeightedQuickUnion wqu;
private int GetVal(int i,int j) {
return (i - 1) * n + j;
}
public Percolation(int n, int opt) {
if(n <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("n is not a postive number.");
this.n = n;
this.opt = opt;
a = new int[n + 2][n + 2];
if(opt == 0) qf = new QuickFind(n * n + 2);
else wqu = new WeightedQuickUnion(n * n + 2);
a[1][0] = a[n][n + 1] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) this.a[i][j] = -1;
}
}
public void Open(int i, int j) {
if(i > n || i < 1 || j > n || j < 1) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("i or j are not in the correct range.");
if(a[i][j] != 0) {
a[i][j] = 0;
if(opt == 0) {
if(i == 1) qf.Union(GetVal(1, 0), GetVal(i, j));
else if(i == n) qf.Union(GetVal(n, n + 1),GetVal(i, j));
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if(x > n || x < 1 || y > n || y < 1 || this.a[x][y] == -1) continue;
qf.Union(GetVal(x, y),GetVal(i, j));
}
}
else {
if(i == 1) wqu.Union(GetVal(1, 0), GetVal(i, j));
else if(i == n) wqu.Union(GetVal(n, n + 1),GetVal(i, j));
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if(x > n || x < 1 || y > n || y < 1 || this.a[x][y] == -1) continue;
wqu.Union(GetVal(x, y),GetVal(i, j));
}
}
}
}
public boolean IsOpen(int i, int j) {
if(i > n || i < 1 || j > n || j < 1) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("i or j are not in the correct range.");
return this.a[i][j] == 0;
}
public boolean IsFull(int i, int j) {
if(i > n || i < 1 || j > n || j < 1) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("i or j are not in the correct range.");
return this.a[i][j] == 1;
}
public boolean Percolates(int opt) {
if(opt == 0) return qf.Connected(0, n*n+1);
return wqu.Connected(0, n*n+1);
}
}
PercolationStats 类
package percolation;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdStats;
public class PercolationStats {
private int n, t;
private double mean, stddev, confidenceLo, confidenceHi;
private double[] data;
public PercolationStats(int n, int t, int opt) {
if(n <= 0 || t <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.n = n;
this.t = t;
if(n == 1) {
mean = 1;
stddev = Double.NaN;
confidenceLo = Double.NaN;
confidenceHi = Double.NaN;
}
else {
data = new double[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Percolation percolation = new Percolation(n, opt);
int num_open = 0;
while(!percolation.Percolates(opt)) {
int row = StdRandom.uniformInt(n) + 1;
int col = StdRandom.uniformInt(n) + 1;
if(!percolation.IsOpen(row, col)) {
percolation.Open(row, col);
num_open++;
}
}
data[i] = 1.0 * num_open / (n * n);
}
mean = StdStats.mean(data);
stddev = StdStats.stddev(data);
confidenceLo = mean - 1.96 * stddev / Math.sqrt(t);
confidenceHi = mean + 1.96 * stddev / Math.sqrt(t);
}
}
public double GetN() {
return n;
}
public double GetT() {
return t;
}
public double Mean() {
return mean;
}
public double Stddev() {
return stddev;
}
public double ConfidenceLo() {
return confidenceLo;
}
public double ConfidenceHi() {
return confidenceHi;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 2000, t = 50;
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
if(i == 0) System.out.println("The algorithm now used is Quick_Find.");
else System.out.println("The algorithm now used is Weighted_Quick_Union.");
long starttime = System.nanoTime();
PercolationStats percolationstats = new PercolationStats(n, t, i);
System.out.println("Mean is :" + percolationstats.Mean());
System.out.println("Stddev is : " + percolationstats.Stddev());
System.out.println("ConfidenceLo is :" + percolationstats.ConfidenceLo());
System.out.println("ConfidenceHi is :" + percolationstats.ConfidenceHi());
long endtime = System.nanoTime();
double cost_time = 1.0 * (endtime - starttime) / 1000000.0;
System.out.println("The cost of time is :" + cost_time + " ms.");
}
}
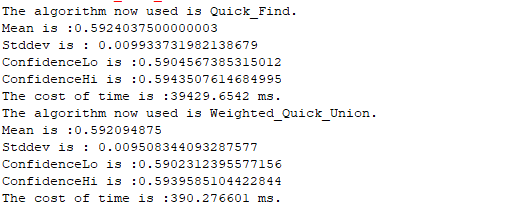
}运行示例
$N=200,T=100$ 时的运行结果。