算法课的第二次实验。
实验内容:排序算法性能比较
问题分析
其实没啥好分析的,就是让比较五种排序算法:插入排序、自顶向下归并排序、自底向上归并排序、随机快速排序、Dijkstra 3-路划分快速排序。
代码
Sort 类
五个排序算法共用的一些方法。
package sortcomparision;
public class Sort {
// Return true if x < y.
protected static boolean Less(Comparable x, Comparable y) {
return x.compareTo(y) < 0;
}
// Return true if x > y.
protected static boolean More(Comparable x, Comparable y) {
return x.compareTo(y) > 0;
}
// Swap a[i] and a[j].
protected static void Exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
Comparable temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
protected static boolean Issorted(Comparable[] a) {
int n = a.length;
for(int i = 0; i+1 < n ; i++) if(More(a[i], a[i+1])) return false;
return true;
}
}IS 类
插入排序
package sortcomparision;
public class IS extends Sort {
public static void Sort(Comparable[] a) {
int n = a.length;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = i; j > 0 && Less(a[j], a[j-1]); j --) Exch(a, j, j-1);
}
}
}TDM 类
自顶向下归并排序
package sortcomparision;
public class TDM extends Sort {
// Merge a[lo...mid] and a[mid+1...hi]
private static void Merge(Comparable[] a, Comparable[] aux, int lo, int mid, int hi) {
for(int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) aux[k] = a[k];
int i = lo, j = mid + 1;
for(int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) {
if (i > mid) a[k] = aux[j++];
else if(j > hi) a[k] = aux[i++];
else if(Less(aux[i], aux[j])) a[k] = aux[i++];
else a[k] = aux[j++];
}
}
// Mergesort a[lo...hi]
private static void Sort(Comparable[] a,Comparable[] aux, int lo, int hi) {
if(hi <= lo) return ;
int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
Sort(a, aux, lo, mid);
Sort(a, aux, mid+1, hi);
Merge(a, aux, lo, mid, hi);
}
public static void Sort(Comparable[] a) {
Comparable[] aux = new Comparable[a.length];
Sort(a, aux, 0, a.length - 1);
}
}
BUM类
自底向上归并排序
package sortcomparision;
public class BUM extends Sort {
// Merge a[lo...mid] and a[mid+1...hi]
private static void Merge(Comparable[] a, Comparable[] aux, int lo, int mid, int hi) {
for(int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) aux[k] = a[k];
int i = lo, j = mid + 1;
for(int k = lo; k <= hi; k ++) {
if(i > mid) a[k] = aux[j++];
else if(j > hi) a[k] = aux[i++];
else if(Less(aux[i], aux[j])) a[k] = aux[i++];
else a[k] = aux[j++];
}
}
public static void Sort(Comparable[] a) {
Comparable[] aux = new Comparable[a.length];
int n = a.length;
for(int len = 1; len < n; len *= 2) {
for(int lo = 0; lo < n - len; lo += len + len) {
int mid = lo + len -1;
int hi = Math.min(lo + len + len - 1, n - 1);
Merge(a, aux, lo, mid, hi);
}
}
}
}
RQ 类
随机快速排序
package sortcomparision;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom;
public class RQ extends Sort {
public static void Sort(Comparable[] a) {
StdRandom.shuffle(a);
Sort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
private static void Sort(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
if(hi <= lo) return ;
int j = Partition(a, lo, hi);
Sort(a, lo, j-1);
Sort(a, j+1, hi);
}
private static int Partition(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
int i = lo;
int j = hi + 1;
Comparable v = a[lo];
while(true) {
while(Less(a[++i], v)) {
if(i == hi) break;
}
while(Less(v, a[--j])) {
if(j == lo) break;
}
if(i >= j) break;
Exch(a, i, j);
}
Exch(a, lo, j);
return j;
}
}QD3P 类
Dijkstra 3-路划分排序
package sortcomparision;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom;
public class QD3P extends Sort {
public static void Sort(Comparable[] a) {
StdRandom.shuffle(a);
Sort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
private static void Sort(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
if(hi <= lo) return ;
int lt = lo, gt = hi;
Comparable v = a[lo];
int i = lo + 1;
while(i <= gt) {
int cmp = a[i].compareTo(v);
if(cmp < 0) Exch(a, lt++, i++);
else if(cmp > 0) Exch(a, i, gt--);
else i++;
}
Sort(a, lo, lt - 1);
Sort(a, gt + 1, hi);
}
}SortComparision 类
排序比较的类。
过程中出现了许许多多的问题,所以对症下药对代码进行了很多的修改。
第一次出现了十次的运行结果中,前几次的运行时间相较于后面的差异过大,把这个问题甩给大模型,说是需要进行“预热”,于是我便在每种排序算法统计其运行时间与内存之前运行三遍而不统计其运行时间与内存。如此操作过后,该问题有了明显的改善。
第二次出现了内存统计时出现的前几次运行的内存相较于后面的差异过大的问题,把这个问题甩给大问题,说是由于 JVM 自身特性的问题,改了半天该问题仍解决不了。于是想了一个笨方法,运行 14 次,只取中间的十组结果,删去最小的两个和最大的两个。如此操作过后,该问题也有了明显的改善。
package sortcomparision;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom;
public class SortComparision {
private static long starttime, endtime, startmemory, endmemory;
private static double costtime, costmemory;
private static Runtime runtime;
private static Comparable[] array;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 10000, maxn = 10000;
System.out.println("The scale of the data is : " + n);
System.out.println("Each number does not exceed : " + maxn);
array = new Comparable[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) array[i] = StdRandom.uniformInt(maxn);
//In order or not
// Arrays.sort(array);
// Insertion Sort
IS();
//Top-down Mergesort
TDM();
// Bottom-up Mergesort
BUM();
// Random Quicksort
RQ();
// Quicksort with Dijkstra 3-way Partition
QD3P();
}
private static void IS() {
Comparable[] a;
runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
System.out.println("Insertion sort :");
ArrayList<Double> times = new ArrayList<>(), memorys = new ArrayList<>();
double averagetime = 0, averagememory = 0;
// Warm-up
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
a = array.clone();
IS.Sort(a);
}
System.gc();
//Time
for(int i = 0; i < 14; i++) {
a = array.clone();
starttime = System.nanoTime();
IS.Sort(a);
endtime = System.nanoTime();
costtime = 1.0 * (endtime - starttime) / 1000000.0;
times.add(costtime);
}
System.gc();
//Memory
for(int i = 0; i < 14; i++) {
System.gc();
a = array.clone();
runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
runtime.gc();
startmemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
IS.Sort(a);
endmemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
costmemory = 1.0 * (endmemory - startmemory) / 1024.0;
memorys.add(costmemory);
}
Collections.sort(times);
times.remove(0);
times.remove(times.size() - 1);
times.remove(0);
times.remove(times.size() - 1);
Collections.sort(memorys);
memorys.remove(0);
memorys.remove(memorys.size() - 1);
memorys.remove(0);
memorys.remove(memorys.size() - 1);
for(Double time : times) {
System.out.print(time + " ");
averagetime += time;
}
averagetime /= 10.0;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The average of time is " + averagetime);
for(Double memory : memorys) {
System.out.print(memory + " ");
averagememory += memory;
}
averagememory /= 10.0;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The average of memory is " + averagememory);
}
private static void TDM() {
Comparable[] a;
runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
System.out.println("Top-down mergesort :");
ArrayList<Double> times = new ArrayList<>(), memorys = new ArrayList<>();
double averagetime = 0, averagememory = 0;
//Warm-up
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
a = array.clone();
TDM.Sort(a);
}
System.gc();
//Time
for(int i = 0; i < 14; i++) {
a = array.clone();
starttime = System.nanoTime();
TDM.Sort(a);
endtime = System.nanoTime();
costtime = 1.0 * (endtime - starttime) / 1000000.0;
times.add(costtime);
}
System.gc();
//Memory
for(int i = 0; i < 14
; i++) {
a = array.clone();
System.gc();
runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
runtime.gc();
startmemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
TDM.Sort(a);
endmemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
costmemory = 1.0 * (endmemory - startmemory) / 1024.0;
memorys.add(costmemory);
}
Collections.sort(times);
times.remove(0);
times.remove(times.size() - 1);
times.remove(0);
times.remove(times.size() - 1);
Collections.sort(memorys);
memorys.remove(0);
memorys.remove(memorys.size() - 1);
memorys.remove(0);
memorys.remove(memorys.size() - 1);
for(Double time : times) {
System.out.print(time + " ");
averagetime += time;
}
averagetime /= 10.0;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The average of time is " + averagetime);
for(Double memory : memorys) {
System.out.print(memory + " ");
averagememory += memory;
}
averagememory /= 10.0;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The average of memory is " + averagememory);
}
private static void BUM() {
Comparable[] a;
runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
System.out.println("Bottom-up mergesort :");
ArrayList<Double> times = new ArrayList<>(), memorys = new ArrayList<>();
double averagetime = 0, averagememory = 0;
// Warm-up
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
a = array.clone();
BUM.Sort(a);
}
System.gc();
//Time
for(int i = 0; i < 14; i++) {
a = array.clone();
starttime = System.nanoTime();
BUM.Sort(a);
endtime = System.nanoTime();
costtime = 1.0 * (endtime - starttime) / 1000000.0;
times.add(costtime);
}
System.gc();
//Memory
for(int i = 0; i < 14; i++) {
a = array.clone();
System.gc();
runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
runtime.gc();
startmemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
BUM.Sort(a);
endmemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
costmemory = 1.0 * (endmemory - startmemory) / 1024.0;
memorys.add(costmemory);
}
Collections.sort(times);
times.remove(0);
times.remove(times.size() - 1);
times.remove(0);
times.remove(times.size() - 1);
Collections.sort(memorys);
memorys.remove(0);
memorys.remove(memorys.size() - 1);
memorys.remove(0);
memorys.remove(memorys.size() - 1);
for(Double time : times) {
System.out.print(time + " ");
averagetime += time;
}
averagetime /= 10.0;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The average of time is " + averagetime);
for(Double memory : memorys) {
System.out.print(memory + " ");
averagememory += memory;
}
averagememory /= 10.0;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The average of memory is " + averagememory);
}
private static void RQ() {
Comparable[] a;
runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
System.out.println("Random quicksort :");
ArrayList<Double> times = new ArrayList<>(), memorys = new ArrayList<>();
double averagetime = 0, averagememory = 0;
// Warm-up
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
a = array.clone();
RQ.Sort(a);
}
System.gc();
//Time
for(int i = 0; i < 14; i++) {
a = array.clone();
starttime = System.nanoTime();
RQ.Sort(a);
endtime = System.nanoTime();
costtime = 1.0 * (endtime - starttime) / 1000000.0;
times.add(costtime);
}
System.gc();
//Memory
for(int i = 0; i < 14; i++) {
System.gc();
a = array.clone();
runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
runtime.gc();
startmemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
RQ.Sort(a);
endmemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
costmemory = 1.0 * (endmemory - startmemory) / 1024.0;
memorys.add(costmemory);
}
Collections.sort(times);
times.remove(0);
times.remove(times.size() - 1);
times.remove(0);
times.remove(times.size() - 1);
Collections.sort(memorys);
memorys.remove(0);
memorys.remove(memorys.size() - 1);
memorys.remove(0);
memorys.remove(memorys.size() - 1);
for(Double time : times) {
System.out.print(time + " ");
averagetime += time;
}
averagetime /= 10.0;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The average of time is " + averagetime);
for(Double memory : memorys) {
System.out.print(memory + " ");
averagememory += memory;
}
averagememory /= 10.0;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The average of memory is " + averagememory);
}
private static void QD3P() {
Comparable[] a;
runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
System.out.println("Quicksort with dijkstra 3-way partition :");
ArrayList<Double> times = new ArrayList<>(), memorys = new ArrayList<>();
double averagetime = 0, averagememory = 0;
// Warm-up
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
a = array.clone();
QD3P.Sort(a);
}
System.gc();
//Time
for(int i = 0; i < 14; i++) {
a = array.clone();
starttime = System.nanoTime();
QD3P.Sort(a);
endtime = System.nanoTime();
costtime = 1.0 * (endtime - starttime) / 1000000.0;
times.add(costtime);
}
System.gc();
//Memory
for(int i = 0; i < 14; i++) {
System.gc();
a = array.clone();
runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
runtime.gc();
startmemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
QD3P.Sort(a);
endmemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
costmemory = 1.0 * (endmemory - startmemory) / 1024.0;
memorys.add(costmemory);
}
Collections.sort(times);
times.remove(0);
times.remove(times.size() - 1);
times.remove(0);
times.remove(times.size() - 1);
Collections.sort(memorys);
memorys.remove(0);
memorys.remove(memorys.size() - 1);
memorys.remove(0);
memorys.remove(memorys.size() - 1);
for(Double time : times) {
System.out.print(time + " ");
averagetime += time;
}
averagetime /= 10.0;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The average of time is " + averagetime);
for(Double memory : memorys) {
System.out.print(memory + " ");
averagememory += memory;
}
averagememory /= 10.0;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The average of memory is " + averagememory);
}
}运行示例
当 $n = 10000$ 时的运行结果。
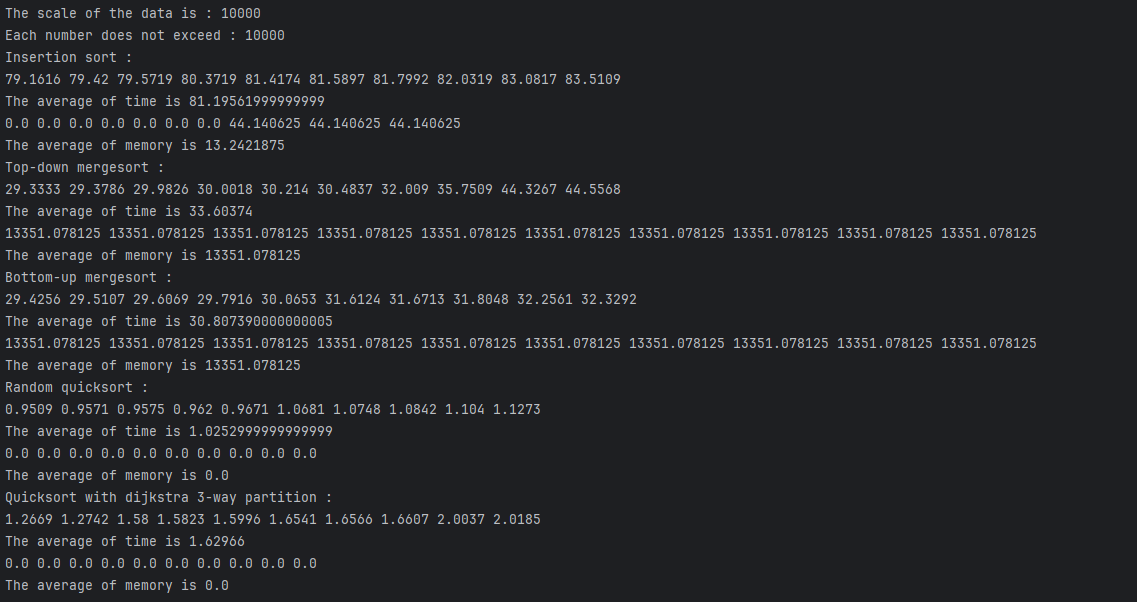
结果分析
$n = 10000, m = 10000$ 的随机数据:
时间(ms)
| Algorithm | Run1 | Run2 | Run3 | Run4 | Run5 | Run6 | Run7 | Run8 | Run9 | Run10 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | 78.1742 | 78.2217 | 78.2672 | 78.8259 | 79.4788 | 79.6742 | 80.6613 | 81.1358 | 81.8563 | 82.0587 | 79.8354 |
| TDM | 1.7701 | 1.7865 | 1.8018 | 1.8056 | 1.8112 | 1.8126 | 1.8502 | 1.8706 | 1.9171 | 1.9517 | 1.8377 |
| BUM | 2.2008 | 2.2198 | 2.231 | 2.2338 | 2.2364 | 2.2476 | 2.3199 | 2.4598 | 2.513 | 2.5737 | 2.3235 |
| RQ | 0.9425 | 0.9759 | 0.9765 | 1.003 | 1.0515 | 1.0676 | 1.0926 | 1.1311 | 1.1325 | 1.15 | 1.0523 |
| QD3P | 1.2457 | 1.3571 | 1.5772 | 1.5973 | 1.6016 | 1.6072 | 1.6173 | 1.6359 | 1.6536 | 1.6878 | 1.5580 |
内存(kb)
| Algorithm | Run1 | Run2 | Run3 | Run4 | Run5 | Run6 | Run7 | Run8 | Run9 | Run10 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| TDM | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 42.2812 | 41.7046 |
| BUM | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 42.125 | 41.6890 |
| RQ | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| QD3P | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
$n = 10000, m = 10000$ 的有序数据:
时间(ms)
| Algorithm | Run1 | Run2 | Run3 | Run4 | Run5 | Run6 | Run7 | Run8 | Run9 | Run10 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | 0.0875 | 0.0882 | 0.0892 | 0.0901 | 0.0933 | 0.0983 | 0.0994 | 0.1170 | 0.2056 | 0.2182 | 0.1187 |
| TDM | 1.2556 | 1.5064 | 1.5126 | 1.5231 | 1.5413 | 1.5434 | 1.5447 | 1.5502 | 1.5574 | 1.6174 | 1.5152 |
| BUM | 0.6212 | 0.6230 | 0.6593 | 0.6623 | 1.5576 | 1.5694 | 1.6623 | 1.6695 | 1.7059 | 1.7538 | 1.2484 |
| RQ | 26.367 | 26.5319 | 26.5819 | 26.7042 | 26.7876 | 26.8839 | 26.9033 | 27.2286 | 27.2362 | 27.2561 | 26.8480 |
| QD3P | 3.8221 | 3.8244 | 3.8339 | 3.8370 | 3.8551 | 3.8702 | 3.8931 | 3.9123 | 3.9588 | 4.4890 | 3.9296 |
内存(kb)
| Algorithm | Run1 | Run2 | Run3 | Run4 | Run5 | Run6 | Run7 | Run8 | Run9 | Run10 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| TDM | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 42.2734 | 41.7039 |
| BUM | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 42.1250 | 41.6891 |
| RQ | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| QD3P | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
$n=10000, m=2$ 的随机数据:
时间(ms)
| Algorithm | Run1 | Run2 | Run3 | Run4 | Run5 | Run6 | Run7 | Run8 | Run9 | Run10 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | 40.6978 | 40.7698 | 41.1507 | 41.2117 | 41.4100 | 41.4837 | 42.6572 | 43.1634 | 43.3091 | 45.9054 | 42.1759 |
| TDM | 0.6344 | 0.6712 | 0.6936 | 0.8629 | 1.6545 | 1.6591 | 1.6774 | 1.6917 | 1.7033 | 1.7120 | 1.2960 |
| BUM | 0.6935 | 0.7106 | 0.7383 | 0.7546 | 1.1552 | 1.6559 | 1.6620 | 1.7027 | 1.9278 | 1.9723 | 1.2973 |
| RQ | 0.8712 | 0.8794 | 0.8815 | 0.8816 | 0.8926 | 1.0298 | 1.0507 | 1.0679 | 1.1060 | 1.1900 | 0.9851 |
| QD3P | 0.1116 | 0.1117 | 0.1117 | 0.1126 | 0.1130 | 0.1133 | 0.1144 | 0.1299 | 0.1351 | 0.1395 | 0.1193 |
内存(kb)
| Algorithm | Run1 | Run2 | Run3 | Run4 | Run5 | Run6 | Run7 | Run8 | Run9 | Run10 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| TDM | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 42.2813 | 41.7047 |
| BUM | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 41.6406 | 42.1250 | 41.6891 |
| RQ | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| QD3P | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
$n=1000, m=10000$ 的随机数据:
时间(ms)
| Algorithm | Run1 | Run2 | Run3 | Run4 | Run5 | Run6 | Run7 | Run8 | Run9 | Run10 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | 0.7968 | 0.7976 | 0.7998 | 0.8015 | 0.8105 | 0.8347 | 0.8520 | 0.8883 | 0.9513 | 1.0686 | 0.8601 |
| TDM | 0.1656 | 0.1657 | 0.1657 | 0.1657 | 0.1659 | 0.1660 | 0.1661 | 0.1679 | 0.1679 | 0.1701 | 0.1667 |
| BUM | 0.1891 | 0.1891 | 0.1892 | 0.1894 | 0.1897 | 0.1899 | 0.1907 | 0.1917 | 0.1986 | 0.2003 | 0.1918 |
| RQ | 0.1357 | 0.1363 | 0.1371 | 0.1375 | 0.1377 | 0.1381 | 0.1382 | 0.1385 | 0.1392 | 0.1541 | 0.1392 |
| QD3P | 0.1372 | 0.1390 | 0.1398 | 0.1420 | 0.1428 | 0.1428 | 0.1436 | 0.1442 | 0.1448 | 0.1457 | 0.1422 |
内存(kb)
| Algorithm | Run1 | Run2 | Run3 | Run4 | Run5 | Run6 | Run7 | Run8 | Run9 | Run10 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| TDM | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 |
| BUM | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 | 6.4844 |
| RQ | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| QD3P | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
问题回答
-
Which sort worked best on data in constant or increasing order (i.e., already sorted data)? Why do you think this sort worked best?
见上表,有序数据的情况下最优的是插入排序。
插入排序在有序的情况下时间复杂度为 $O(n)$ 。
-
Did the same sort do well on the case of mostly sorted data? Why or why not?
不一定。例如随机快排,在有序的情况下会退化到 $O(n^2)$。
-
In general, did the ordering of the incoming data affect the performance of the sorting algorithms? Please answer this question by referencing specific data from your table to support your answer.
会影响。
如上表,在同等规模的随机数据和有序数据下,随机快排在随机数据的平均运行时间为 1.0523ms,而有序数据为 26.8480ms。
-
Which sort did best on the shorter (i.e., n = 1,000) data sets? Did the same one do better on the longer (i.e., n = 100,000) data sets? Why or why not? Please use specific data from your table to support your answer.
随机数据最快为 QD3P,有序数据最快为 IS。数据规模较小时,几种排序效率差不多。
-
In general, which sort did better? Give a hypothesis as to why the difference in performance exists.
QD3P。相较于 RQ,能处理更多的情况。
-
Are there results in your table that seem to be inconsistent? (e.g., If I get run times for a sort that look like this {1.3, 1.5, 1.6, 7.0, 1.2, 1.6, 1.4, 1.8, 2.0, 1.5] the 7.0 entry is not consistent with the rest). Why do you think this happened?
存在这样的情况。我的猜测是与 JVM 本身运行过程的一些特性有关。我的处理方法是剔除掉这些明显异常的值。
